Top 15 Must-Have Skills for Today’s Librarian
The role of the modern librarian has evolved dramatically from the traditional image of book custodians enforcing silence. Today’s librarians are dynamic navigators of complex information ecosystems, technology integrators, community builders, and advocates for information equity. As the International Federation of Library Associations (IFLA) emphasized in its 2024 Trend Report, library professionals must embrace a skills agenda that aligns with emerging trends in knowledge creation, technological transformation, and evolving community needs (3).
emphasized in its 2024 Trend Report, library professionals must embrace a skills agenda that aligns with emerging trends in knowledge creation, technological transformation, and evolving community needs (3).
- Digital Literacy and Technological Proficiency
Digital literacy encompasses the ability to find, evaluate, and create content using information technologies and the internet (5). Modern librarians must be proficient with digital tools, databases, e-books, audiobooks, and multimedia platforms. 
How to Acquire: Embrace continuous learning through online courses, professional development workshops, and hands-on practice with digital platforms. Organizations like the American Library Association offer specialized training programs (12).
Benefits: Digital literacy enables librarians to effectively manage digital resources, guide patrons through both physical and digital materials, and teach essential digital skills to library users (12).
2. Data Literacy and Analysis
Data literacy involves understanding how to collect, analyze, interpret, and communicate with data effectively. This skill extends beyond technical analysis to encompass critical thinking about data sources, reliability, and ethical implications (7).
How to Acquire: Complete specialized programs such as the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis’s data literacy course for librarians, which covers seven foundational competencies using real-world data (13). Engage in research partnerships with faculty colleagues to develop practical data analysis  skills (9).
skills (9).
Benefits: Data literacy empowers librarians to understand user behavior, make informed decisions about library services, and support workforce preparation by teaching patrons crucial analytical skills (9).
workforce preparation by teaching patrons crucial analytical skills (9).
3. Information Management and Curation
Information management involves collecting, organizing, maintaining, retrieving, and disseminating information across both physical and digital realms. With information exponentially increasing, libraries serve as crucial hubs for accessing diverse resources (12).
How to Acquire: Pursue formal education through library science programs and gain practical experience through on-the-job training in cataloging, metadata analysis, and knowledge of reference tools (10).
Benefits: Strong information management skills enable librarians to efficiently organize library resources, conduct effective research, and support users in their information-seeking journeys (12).
4. Artificial Intelligence and Emerging Technology Understanding
Understanding AI, machine learning, virtual reality, and augmented reality has become essential as these technologies reshape library services and user experiences (5).
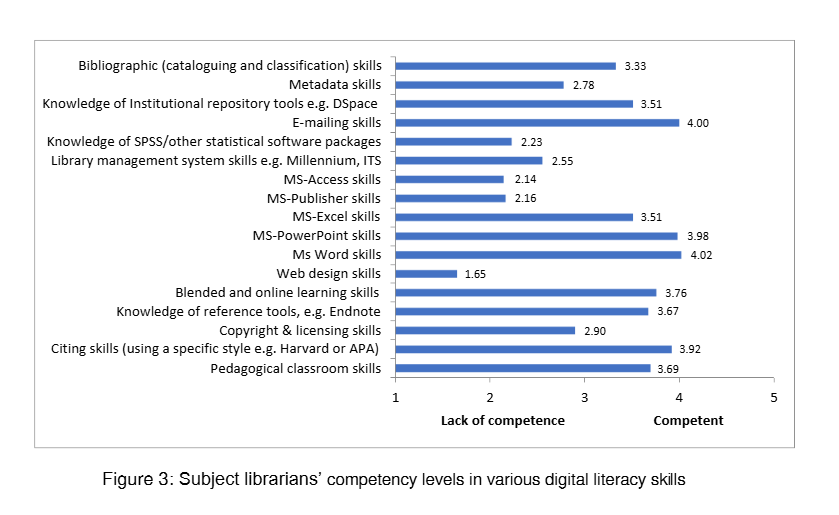
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363652112_Skills_of_Subject_Librarians_for_Digital_Literacy_Instruction_in_Academic_Libraries
How to Acquire: Participate in professional development opportunities like the AI Literacy Resource Hackathon, which brings together librarians to develop educational materials on AI literacy covering technical, practical, and ethical dimensions (8). Engage with professional communities of practice focused on AI applications in libraries.
Benefits: AI literacy enables librarians to implement innovative technologies, provide guidance on algorithmic thinking and digital citizenship, and help users gain a critical understanding of how data and computation affect everyday life (8).
5. Community Engagement and Outreach
Community engagement focuses on cultivating strong ties between libraries and local communities by understanding unique needs, interests, and challenges (19). This skill involves conducting needs assessments, building partnerships, and extending services beyond physical library spaces.
How to Acquire: Develop skills through participatory design training, which ensures community input into programs and services. Participate in community commissions, neighborhood groups, and local organizations to build leadership capabilities (18).
Benefits: Effective community engagement demonstrates library value, increases support and funding, and ensures libraries address actual community needs rather than assumed ones (18).
6. Cultural Competency and Diversity Awareness
Cultural competency is the ability to function with awareness, knowledge, and interpersonal skills when engaging people of different backgrounds, beliefs, values, and behaviors (17). This involves understanding power dynamics, centering people and relationships, and creating belonging for everyone (14). 
How to Acquire: Complete formal training programs, such as sensitivity training workshops and diversity, equity, and inclusion courses. Study frameworks like Nicole Cooke’s comprehensive approach in “Information Services to Diverse Populations” (15). Engage in self-reflection about personal values and biases.
Benefits: Cultural competency enables libraries to serve diverse populations effectively, create inclusive environments where all community members feel comfortable, and address the needs of marginalized groups (16).
7. Programming and Event Planning
Library programming has become central to the modern library’s mission. Programming competency encompasses organizational skills, event planning, creativity, content knowledge, and outreach (1).
How to Acquire: The American Library Association’s Skills for 21st-Century Librarians initiative provides learning objectives across nine core competency areas. Gain experience through peer learning, mentorship, and professional development trainings (1).
Benefits: Strong programming skills enable librarians to create engaging, relevant programs that draw community members into the library and demonstrate the institution’s value beyond traditional services (1).
8. Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Communication skills are crucial for building positive relationships with diverse users, meeting varied needs, and creating welcoming library environments (12). This includes written, verbal, and digital communication abilities.
How to Acquire: Practice active listening, develop presentation skills, and learn culturally centered communication techniques. Participate in customer service training and develop conflict-resolution skills (4).
 Benefits: Excellent communication skills enable librarians to assist patrons effectively, collaborate with colleagues and community partners, and advocate for library resources and services (12).
Benefits: Excellent communication skills enable librarians to assist patrons effectively, collaborate with colleagues and community partners, and advocate for library resources and services (12).
9. Teaching and Instructional Design
Modern librarians must excel at teaching information literacy, research skills, and technology competencies to diverse audiences ranging from children to adults (12).
How to Acquire: Develop pedagogical skills through formal education in library science programs, attend workshops on instructional design, and practice through delivering one-shot sessions and seminars. Study best practices in active learning and assessment (11).
Benefits: Teaching skills empower librarians to guide users in navigating information resources, developing critical thinking abilities, and becoming effective researchers across multiple disciplines (11).
10. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Critical thinking involves analyzing information, evaluating sources, making informed judgments, and solving complex problems creatively (10).
How to Acquire: Cultivate critical thinking through continuous engagement with diverse information sources, participation in professional discussions, and regular reflection on library challenges and solutions—case studies of innovative library practices (4).
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326966235_Innovative_and_creative_skills_for_the_21st_Century_librarian_benefits_and_challenges_in_Nigerian_academic_libraries
Benefits: Critical thinking enables librarians to make sound decisions about collection development, service implementation, and resource allocation while adapting to rapidly changing information environments (6).
11. Marketing and Advocacy
Librarians must effectively market library services, advocate for resources, and demonstrate institutional value to stakeholders and funding bodies (1).
How to Acquire: Learn marketing fundamentals through professional development courses, study successful library campaigns, and develop skills in social media management and public relations. Practice storytelling about library impact (10).
Benefits: Strong marketing and advocacy skills help secure funding, increase library usage, and build community support while demonstrating how libraries contribute to

https://www.ala.org/sites/default/files/pla/content/data/Census_Data_Literacy_Resources.pdf
educational and community goals (4).
12. Project Management and Leadership
Leadership skills enable librarians to influence others, lead teams, create new services, and solve challenges (4).
How to Acquire: Pursue leadership development initiatives, take on progressively responsible roles, and study project management methodologies. Participate in mentorship programs designed to support emerging leaders (16).
Benefits: Leadership and project management skills allow librarians to successfully implement complex initiatives, manage resources effectively, and inspire colleagues toward shared goals (4).
13. Adaptability and Lifelong Learning
Adaptability—the ability to adjust to new conditions and challenges effectively—enables librarians to keep pace with technology trends and continue delivering quality service despite constant change (12).
How to Acquire: Embrace a growth mindset, view change as an opportunity rather than a threat, stay informed about library trends through professional reading, and regularly step outside comfort zones to learn new skills (12).
Benefits: Adaptability ensures librarians remain relevant as roles evolve, builds resilience in the face of challenges, and turns setbacks into learning opportunities (12).
14. Research and Scholarly Communication
Understanding research methodologies, scholarly publishing, open access, and intellectual property enables librarians to support academic and community research effectively (5).
How to Acquire: Study research methods through formal education, stay current with scholarly communication trends, and develop expertise in bibliometrics, citation management tools, and research data management. Collaborate with researchers on projects (5).
Benefits: Research expertise positions librarians as valued partners in the research process, provides practical support for grant applications and publications, and promotes open science initiatives (5).
15. Ethics and Information Equity Advocacy
Librarians must champion information equity, intellectual freedom, and ethical information practices while advocating for social justice and ensuring equitable access regardless

https://www.cde.state.co.us/communications/strategicplan2025-2028
of background (6).
How to Acquire: Study professional ethics codes, engage with discussions about information policy and access, participate in advocacy training, and develop an understanding of privacy, copyright, and licensing issues (10).
Benefits: A firm ethical grounding enables librarians to guarantee that every community member can access necessary information and resources, promote diversity and inclusion, and defend intellectual freedom (6).
The modern librarian’s skill set represents a dynamic blend of traditional information science expertise and contemporary competencies in technology, community engagement, and advocacy. Research indicates that librarians can acquire these skills through formal library science education, on-the-job training, professional development programs, and continuous learning initiatives (2). However, the major challenge for librarians remains inadequate funding to support capacity-building efforts (2).
Despite these challenges, investing in these fifteen essential skills enables librarians to serve as vital catalysts for progress in the 21st century. By mastering digital technologies, fostering inclusive communities, analyzing data effectively, and advocating for information equity, librarians ensure their institutions remain indispensable community assets.
References
- American Library Association. (n.d.). Skills for 21st-Century Librarians. Retrieved from https://www.ala.org/tools/programming/21stcenturyskills
- ResearchGate. (2010). Quickies for the 21st Century Librarian. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282506805_Quickies_for_the_21st_Century_Librarian
- INFOLIBNET. (2025, February 15). IFLA: A Skills Agenda for the Trend Report 2024. Retrieved from https://mylibrarianship.wordpress.com/2025/02/15/ifla-a-skills-agenda-for-the-trend-report-2024/
- ResearchGate. (2018, August 7). Innovative and creative skills for the 21st-century librarian. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326966235_Innovative_and_creative_skills_for_the_21st_Century_librarian_benefits_and_challenges_in_Nigerian_academic_libraries
- INFOLIBNET. (2024, October 23). Embracing the Digital Future: Essential Skills for Librarians in Evolving Work Environments. Retrieved from https://mylibrarianship.wordpress.com/2024/10/23/embracing-the-digital-future-essential-skills-for-librarians-in-evolving-work-environments/
- Atlantis Press. (2024). The Future of Libraries: Skills, Challenges, and Innovative Visions for the Future. Retrieved from https://www.atlantis-press.com/article/126011034.pdf
- UKSG. (2024, October 7). What is data literacy, and why are librarians the best people to support it? Retrieved from https://www.uksg.org/newsletter/what-data-literacy-and-why-are-librarians-best-people-support-it/
- CMU Libraries. (2024). Libraries Elevates AI, Information, and Data Literacy. Retrieved from https://www.library.cmu.edu/about/news/2024-09/poem-ai-data-literacy
- UNH Scholars Repository. (2023). Cultivating a Data Literate Workforce. Retrieved from https://scholars.unh.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2622&context=faculty_pubs
- ResearchGate. (2022, July 27). Skills of Subject Librarians for Digital Literacy Instruction in Academic Libraries. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363652112_Skills_of_Subject_Librarians_for_Digital_Literacy_Instruction_in_Academic_Libraries
- ALA Store. (n.d.). Data Literacy in Academic Libraries: Teaching Critical Thinking with Numbers. Retrieved from https://alastore.ala.org/dataliteracy
- Bolt Jobs. (n.d.). The Top 10 Skills Needed by Librarians in the Digital Age. Retrieved from https://www.boltjobs.com/blog/skills-librarians-need-digital
- American Library Association. (n.d.). Data Literacy. Retrieved from https://literacy.ala.org/data-literacy/
- Library Journal. (2024). How to Build a Library Culture of Belonging. Retrieved from https://www.libraryjournal.com/event/how-to-build-a-library-culture-of-belonging-sep-2024
- ALA Store. (n.d.). Information Services to Diverse Populations: Developing Culturally Competent Library Professionals, Second Edition. Retrieved from https://alastore.ala.org/isdp2
- Liblime. (2024, November 25). Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Libraries: A 2024 Perspective. Retrieved from https://liblime.com/2024/11/25/diversity-equity-and-inclusion-in-libraries-a-2024-perspective/
- ALA Core News. (2024, April 16). Preservation Week Free Webinar on Cultural Competency. Retrieved from https://alacorenews.org/2024/04/16/preservation-week-free-webinar-on-cultural-competency/
- McClellan, R., Córdova, S., & Colorado Department of Education. (2025). Colorado Department of Education Strategic Plan 2025-28. https://www.cde.state.co.us/communications/strategicplan2025-2028
- CareerExplorer. (2023, November 22). What does a community librarian do? Retrieved from https://www.careerexplorer.com/careers/community-librarian/
